
We normally connect to Vagrant boxes over ssh. If networking doesn’t work properly in the guest, due to a misconfiguration or the DHCP server not assigning it an IP address, we have to find another way to login and see what went wrong.
The official CentOS images for Vagrant are preconfigured to use a serial console, but some virtualization providers do not emulate any serial port by default, so we have to enable such a port in our Vagrantfile.
libvirt
The serial port might be enabled by default in libvirt. In this case,
we can simply use virsh console <domain> to connect. If not, we
first have to enable the serial port as described in the
vagrant-libvirt documentation.
VirtualBox
Things are a bit more complicated with Virtualbox. We first need to enable the first serial port in our Vagrantfile and connect it to a socket:
Vagrant.configure(2) do |config|
config.vm.box = "centos/7"
config.vm.synced_folder ".", "/vagrant", disabled: true
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
v.memory = 1024
v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--uart1", "0x3F8", "4"]
v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--uartmode1", "server", "ttyS0.sock"]
end
end
After starting the box, we can use socat to route the UNIX domain
socket created by VirtualBox to a pty device that another program
running on the host will be able to use like a real serial port:
$ socat -d -d ./ttyS0.sock PTY
2017/05/10 22:12:14 socat[1649] N opening connection to LEN=14 AF=1 "./ttyS0.sock"
2017/05/10 22:12:14 socat[1649] N successfully connected from local address LEN=16 AF=1 ""
2017/05/10 22:12:14 socat[1649] N successfully connected via
2017/05/10 22:12:14 socat[1649] N PTY is /dev/ttys002
2017/05/10 22:12:14 socat[1649] N starting data transfer loop with FDs [5,5] and [6,6]
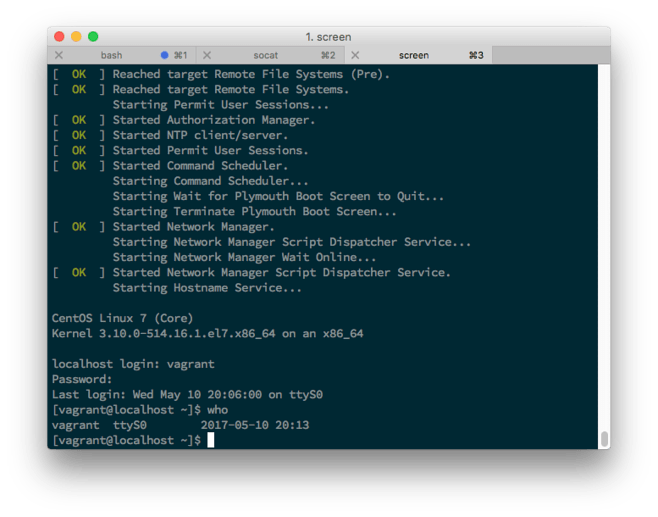
The CentOS Linux images for Vagrant are configured to use the serial
port at a baud rate of 115200, the highest possible. We can use
screen /dev/ttys002 115200,n8 to connect to the serial console and
login:
We could also configure VirtualBox to connect the serial port to a TCP
socket, by changing the second modifyvm line above to v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--uartmode1", "tcpserver", "2323"], and then using
telnet to connect to port 2323 on localhost. This doesn’t require
installing socat, but makes interactive programs annoying to use
(telnet defaults to line mode when connecting to a port different than
23, which will buffer the characters we typed until we press Enter).
That can usually be changed that by adding mode character to our
.telnetrc file – please see the telnet man page for details.

